Reasoning about logic
This article discusses about logic, you know the part that is detached from feelings or emotions in your brain. Dictionaries don’t have one single definition. But, the top definitions that is based on what is commonly understood is, “a way of thinking”, “sensible reasons for doing”. For example, when something is playing but we can’t hear it, we turn up the volume. Another example is, if you don’t have enough money to buy something, you don’t buy it. If you hear someone say, they didn’t have enough and yet they ended up with that thing, you begin to question something. What you are questioning and what’s letting you question, is your logic. Once we understand there are other ways they ended up with that thing, for example, by stealing, we are able to confirm another reason which then sets our logic on the right path.
Logic is also a topic of study in Mathematics and Computer Science. It starts off teaching about establishing the truth of statements. For example, when pointed at a book, you’d say “that is a book” and it is a true statement. If you say “not a book”, it is a false statement. But, when we view a combination of statements, that is when things get a bit complex. Often we have to look at two statements that are true so that both have to be true to establish the overall truth about something. For example you need both a boarding pass and a photo ID in order to enter the gates to board a flight. However you can produce a boarding pass on paper or in a digital form from a phone. This is when we start discussing about logic in the form of “and”/”or”. So, we learn our truth tables:
AND
| Input 1 | Input 2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
OR
| Input 1 | Input 2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |
Using the flight boarding example, we can reason the above truth table and notice that the “and” table applies when we need to be granted access to the gates. The “or” applies when we need to produce the boarding pass but it doesn’t matter in what form. So, we don’t need to blindly accept, “True” and “True” makes a “False”, “True” or “False” makes a “True”. Once we have this understanding, the truth table is fairly intuitive.
The logic of “and”/”or” should be pretty clear from the above explanation. However to understand things a bit more visually, here are two examples for “and”:
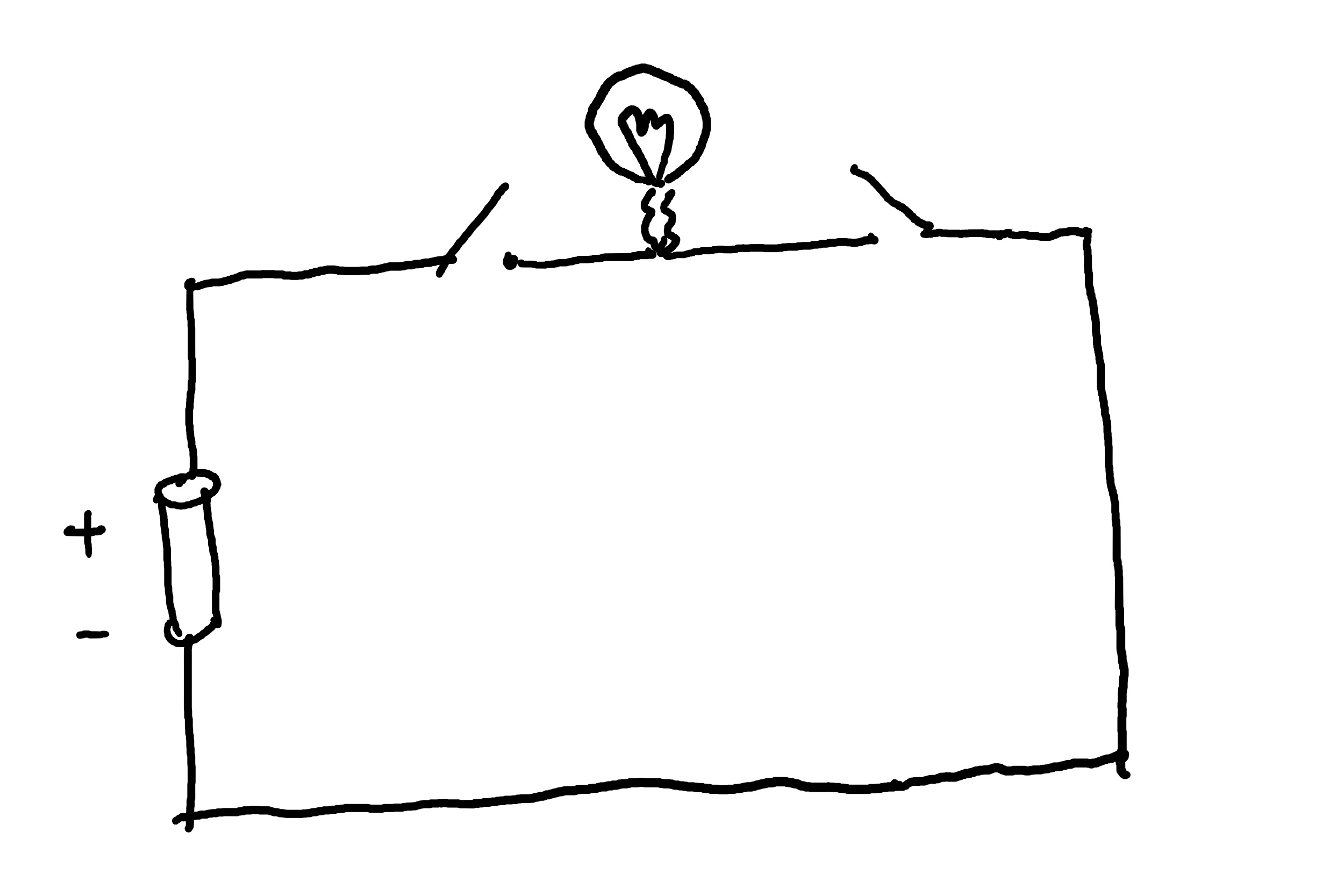 In the above example, in order for the bulb to light up, we need to close both the switches.
In the above example, in order for the bulb to light up, we need to close both the switches.
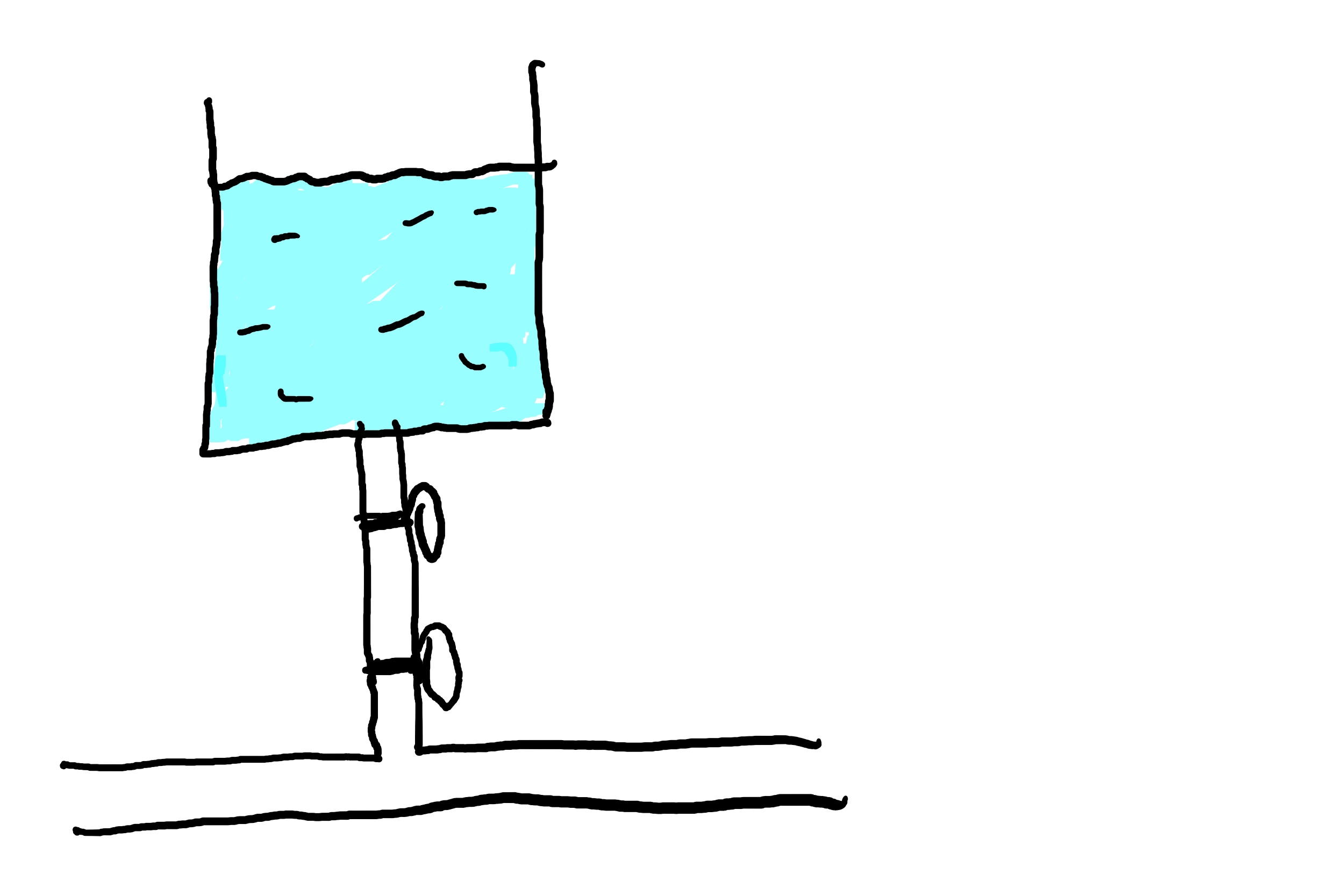 In the above example, in order for the water to flow from the tank through to the main pipe, we need to open both the valves.
In the above example, in order for the water to flow from the tank through to the main pipe, we need to open both the valves.
These are two examples for “or”:
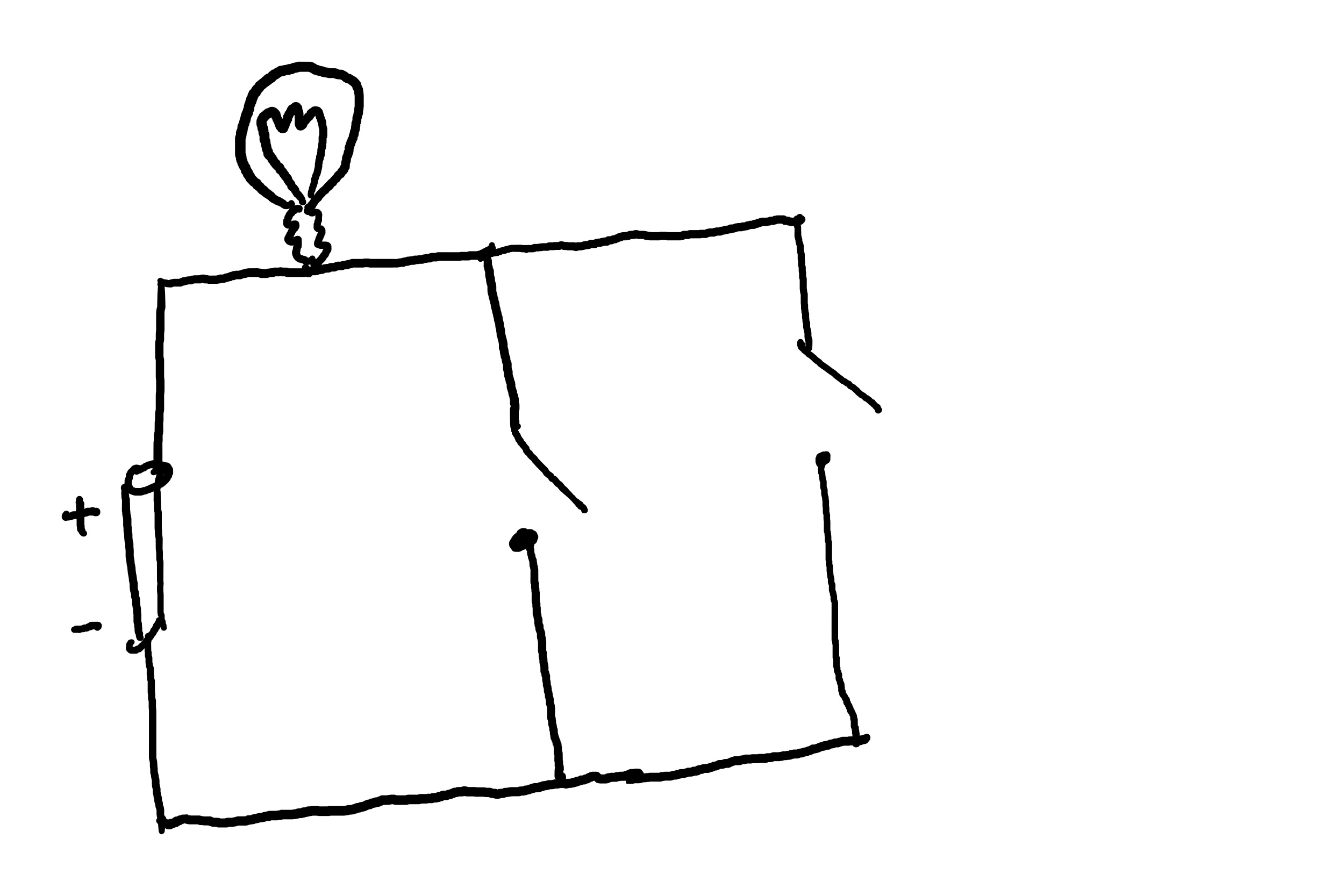 In the above example, in order for the bulb to light up, it is enough to close only one of the switches.
In the above example, in order for the bulb to light up, it is enough to close only one of the switches.
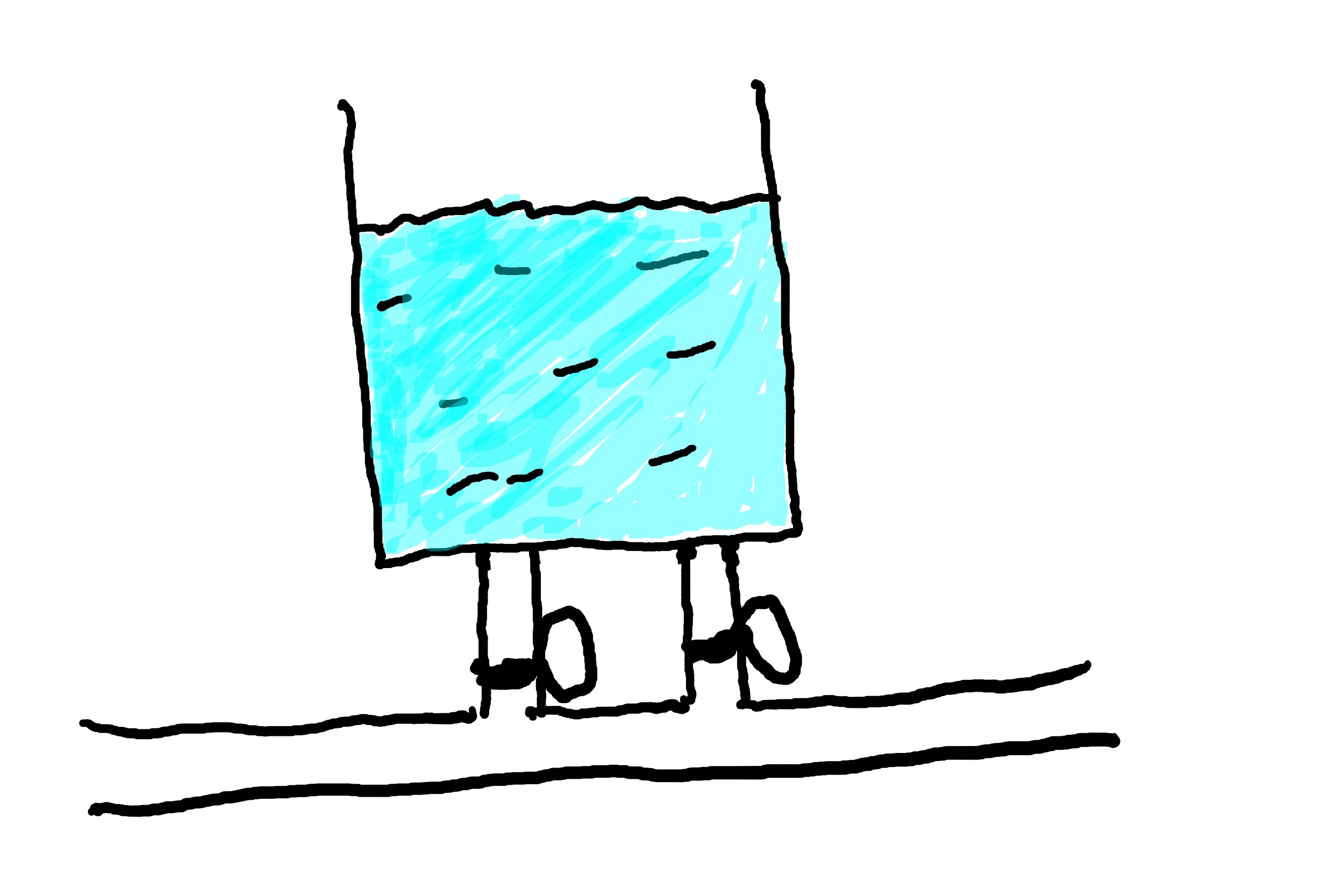 In the above example, in order for the water to flow from the tank through to the main pipe, it is enough to open one of the valves.
In the above example, in order for the water to flow from the tank through to the main pipe, it is enough to open one of the valves.
For a computer to perform logic, we have transistors used as switches and the switch in “on”/”off” positions is treated as “true”/”false” respectively. In different combinations, these can help realize the “and”/”or” logic. This is the basis for developing Boolean Algebra which is applied to build more complex logic in computers that are mostly a combination of multiple “and”/”or”. This provides a way to program the computer so that we can delegate complex decision making through programs we write that will instruct the computer accordingly.
With this understanding I’m sure it is not a long shot to think logically as it is an integral part of our decision making process in every stage of our lives.
